APPLICATION
How does BLDC motor works
How does BLDC motor works
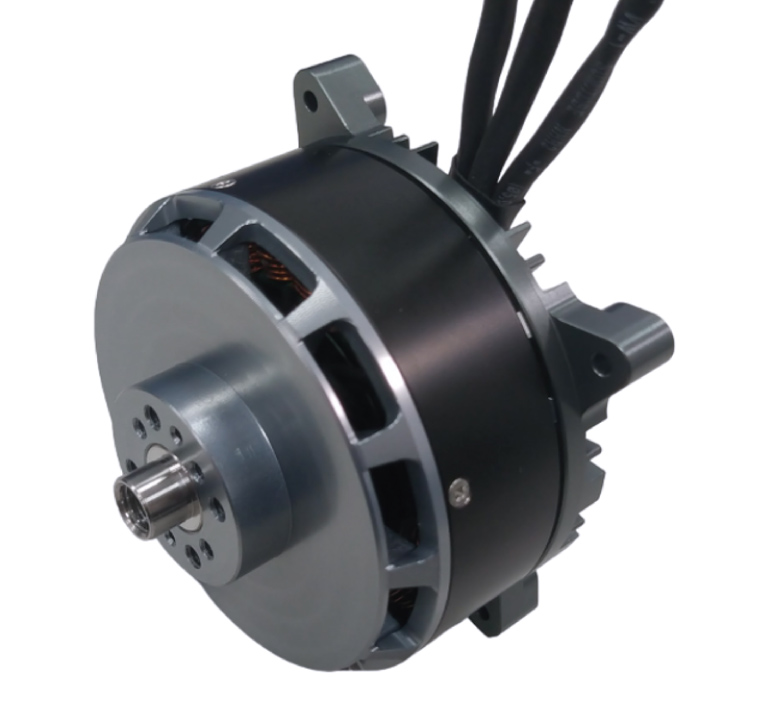

1. Components
- Rotor: The rotating part of the motor, typically containing permanent magnets.
- Stator: The stationary part of the motor, containing electromagnetic coils (windings).
- Electronic Speed Controller (ESC): The "brain" of the motor, responsible for controlling the current flow to the stator windings.
2. Working Principle
- Magnetic Interaction:
- The rotor's permanent magnets create a magnetic field.
- The ESC selectively energizes the stator windings in a specific sequence.
- This creates a rotating magnetic field in the stator.
- The rotor's magnets are attracted to and repelled by the stator's magnetic field, causing the rotor to spin.
- Commutation:
- The ESC constantly monitors the rotor's position (using sensors like Hall Effect sensors).
- Based on the rotor's position, the ESC switches the current to different stator windings.
- This "switching" of current is called commutation.
- Commutation ensures that the rotor is always "chasing" the rotating magnetic field in the stator, maintaining continuous rotation.
3. Key Advantages
- High Efficiency: Reduced friction due to the absence of brushes leads to higher efficiency.
- Long Lifespan: No brush wear and tear extends the motor's lifespan significantly.
- High Speed and Torque: Capable of achieving high speeds and producing high torque.
- Quiet Operation: Smooth and quiet operation due to the absence of brush friction.
In Summary
BLDC motors work by utilizing the interaction between a rotating magnetic field generated by the stator windings and the permanent magnets on the rotor. The electronic speed controller plays a crucial role in controlling the current flow to the stator windings, ensuring efficient and smooth operation.