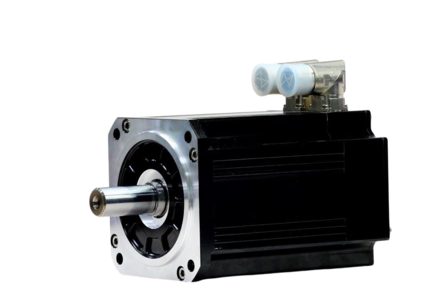
How does DC motor works
How does DC motor works
A DC motor operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When an electric current flows through a conductor placed within a magnetic field, it experiences a force. In a DC motor, this force causes a rotor (the rotating part) to spin. This interaction between the magnetic field and the current flowing through the rotor's coils generates continuous rotation, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
1. Components
- Rotor: The rotating part of the motor. It comprises coils of wire wound around a core.
- Stator: The stationary part of the motor, providing the magnetic field. This can be achieved through permanent magnets or electromagnets.
- Commutator and Brushes: These components ensure the current flowing through the rotor coils changes direction at the appropriate times, maintaining continuous rotation.
2. Working Principle
- Current Flow: When a DC current is supplied to the rotor coils, it generates a magnetic field.
- Magnetic Interaction: This magnetic field interacts with the stator's magnetic field.
- Force Generation: This interaction creates a force that acts on the rotor, causing it to spin.
- Commutation: The commutator and brushes reverse the current direction in the rotor coils at specific intervals, ensuring continuous rotation in the same direction.
3. In Summary
DC motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. They operate by utilizing the interaction between magnetic fields and electric currents. When a current flows through the rotor coils within the stator's magnetic field, a force is generated, causing the rotor to rotate. The commutation process ensures continuous rotation, making DC motors essential in various applications.